Imaging
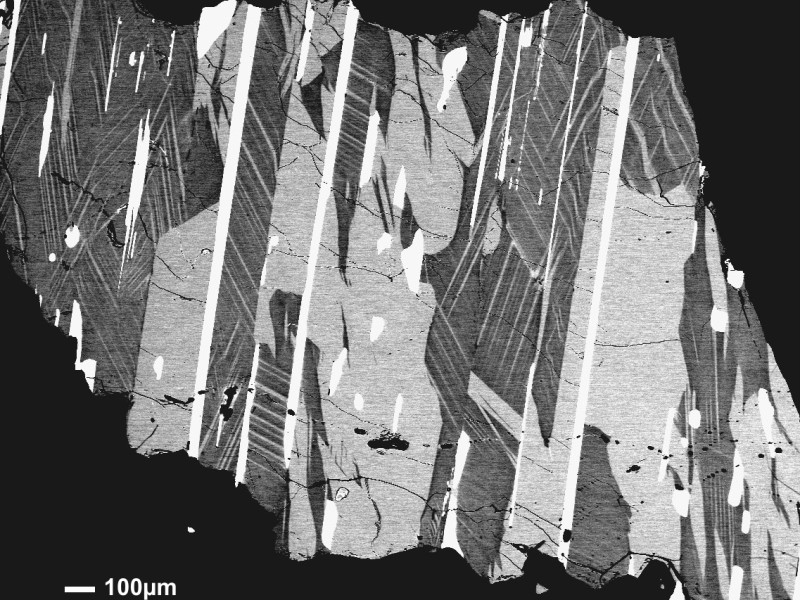
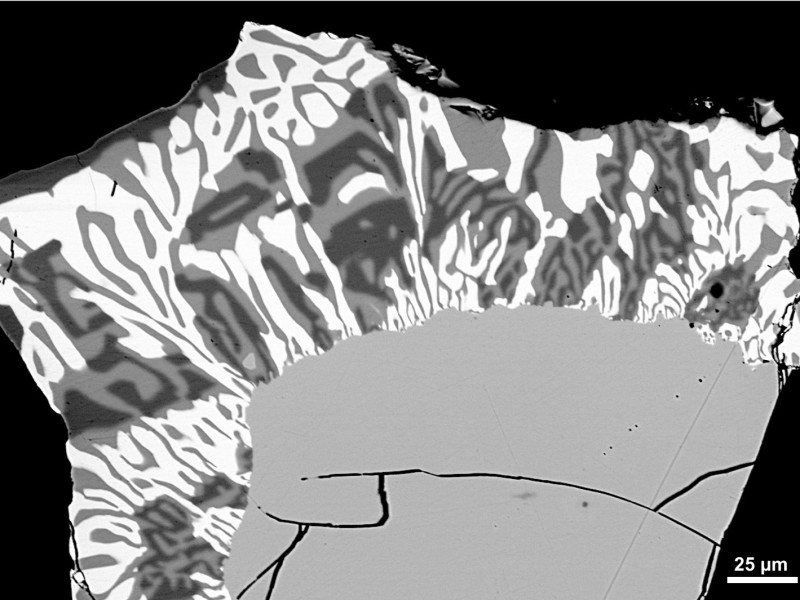
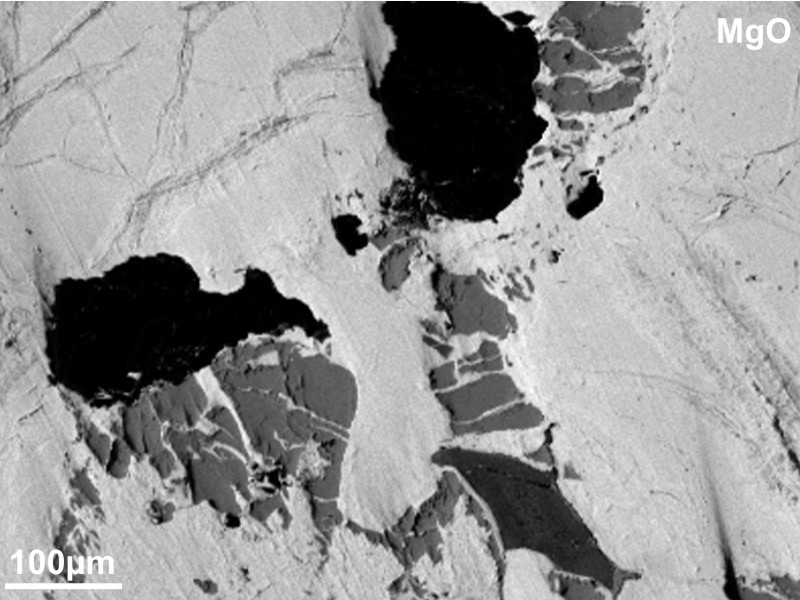
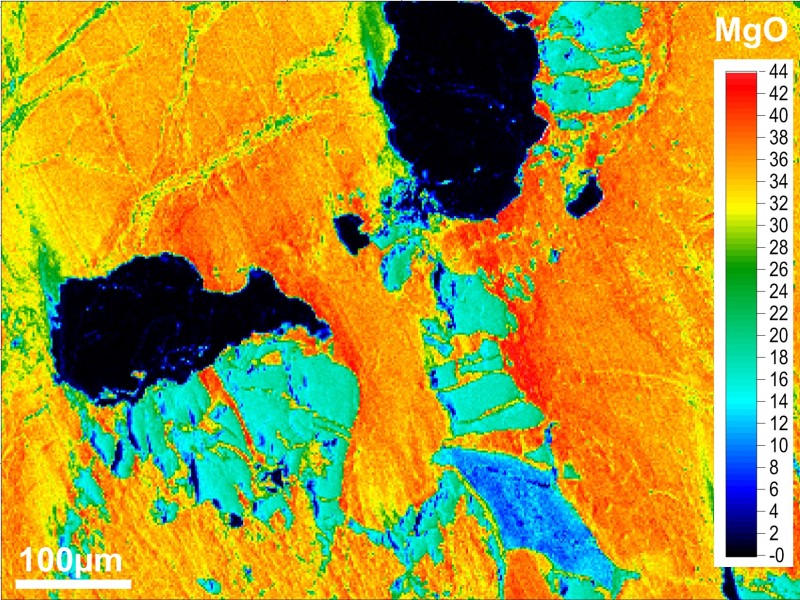
Secondary electron (SE), backscattered electron (BSE), characteristic X-ray, and cathodoluminescence (CL) signals are used to produce images of different information content. By moving the electron beam, or the sample, images can be acquired, processed, and stored digitally. They can be displayed in either grayscale or false color, depending on the scientific question.
Electron images
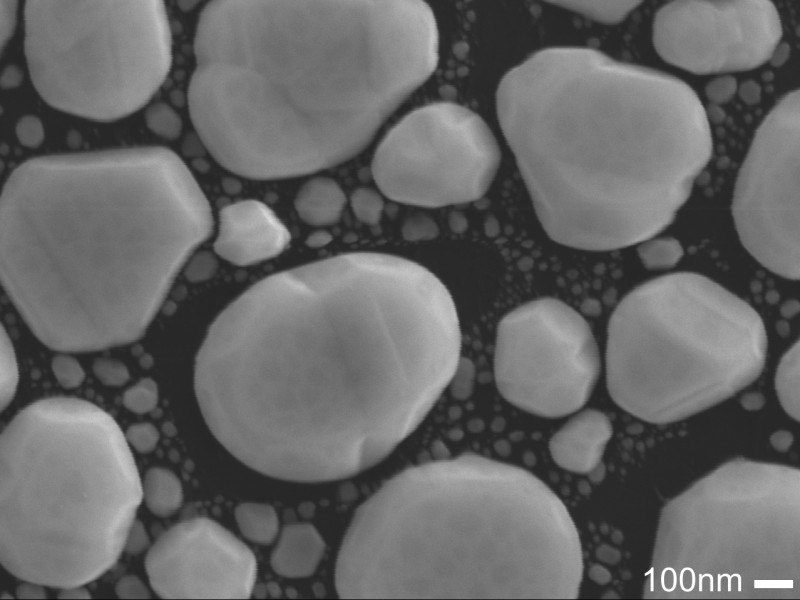
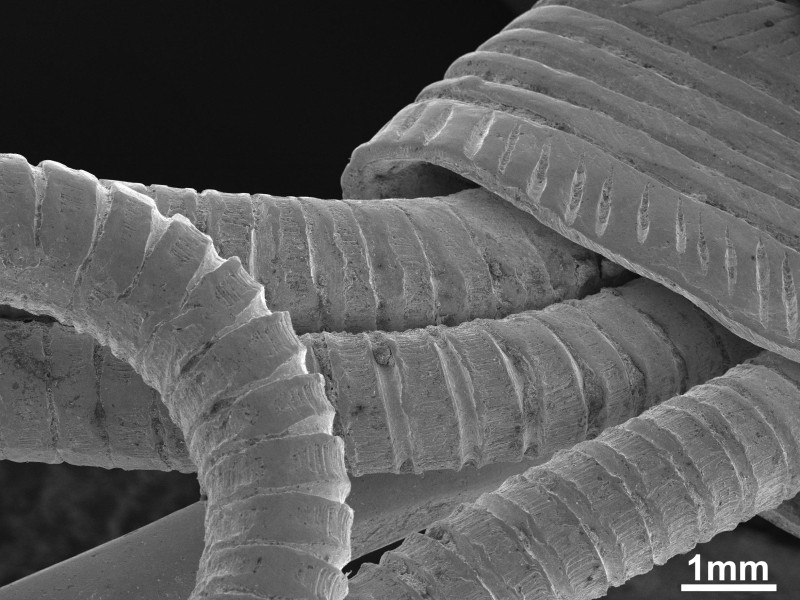
SE imaging provides topographic information of a sample. The spatial resolution for SE imaging is approximately 100 to 200 nm, depending on the accelerating voltage, beam current, and other operating conditions. Common applications include studies of grain morphology, precipitates on a mineral surface, microfossils, biological as well as anthropological samples and other materials too small for visible light microscopy.